How To Create Dbcontext In Entity Framework Core
Creating a Model for an Existing Database in Entity Framework Core
Here you will learn how to create the context and entity classes for an existing database in Entity Framework Core. Creating entity & context classes for an existing database is called Database-First approach.
EF Core does not support visual designer for DB model and wizard to create the entity and context classes similar to EF 6. So, we need to do reverse engineering using the Scaffold-DbContext command. This reverse engineering command creates entity and context classes (by deriving DbContext) based on the schema of the existing database.
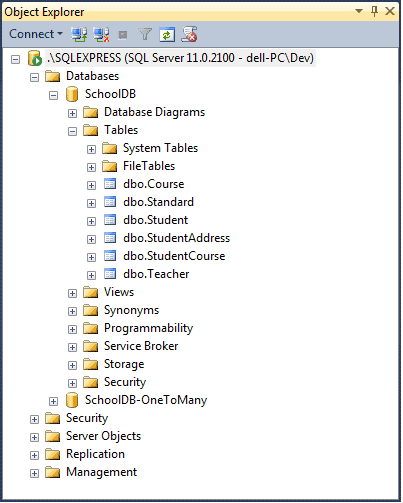
Let's create entity and context classes for the following SchoolDB database in the local MS SQL Server shown below.
Scaffold-DbContext Command
Use Scaffold-DbContext to create a model based on your existing database. The following parameters can be specified with Scaffold-DbContext in Package Manager Console:
Scaffold-DbContext [-Connection] [-Provider] [-OutputDir] [-Context] [-Schemas>] [-Tables>] [-DataAnnotations] [-Force] [-Project] [-StartupProject] [<CommonParameters>] In Visual Studio, select menu Tools -> NuGet Package Manger -> Package Manger Console and run the following command:
PM> Scaffold-DbContext "Server=.\SQLExpress;Database=SchoolDB;Trusted_Connection=True;" Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer -OutputDir Models In the above command, the first parameter is a connection string which includes three parts: DB Server, database name and security info. Here, Server=.\SQLExpress; refers to local SQLEXPRESS database server. Database=SchoolDB; specifies the database name "SchoolDB" for which we are going to create classes. Trusted_Connection=True; specifies the Windows authentication. It will use Windows credentials to connect to the SQL Server. The second parameter is the provider name. We use provider for the SQL Server, so it is Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer. The -OutputDir parameter specifies the directory where we want to generate all the classes which is the Models folder in this case.
Use the following command to get the detailed help on Scaffold-DbContext command:
PM> get-help scaffold-dbcontext –detailed The above Scaffold-DbContext command creates entity classes for each table in the SchoolDB database and context class (by deriving DbContext) with Fluent API configurations for all the entities in the Models folder.
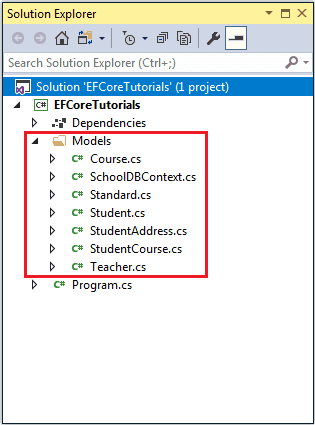
The following is the generated Student entity class for the Student table.
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; namespace EFCoreTutorials.Models { public partial class Student { public Student() { StudentCourse = new HashSet<StudentCourse>(); } public int StudentId { get; set; } public string FirstName { get; set; } public string LastName { get; set; } public int? StandardId { get; set; } public Standard Standard { get; set; } public StudentAddress StudentAddress { get; set; } public ICollection<StudentCourse> StudentCourse { get; set; } } }
The following is the SchoolDBContext class which you can use to save or retrieve data.
using System; using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Metadata; namespace EFCoreTutorials.Models { public partial class SchoolDBContext : DbContext { public virtual DbSet<Course> Course { get; set; } public virtual DbSet<Standard> Standard { get; set; } public virtual DbSet<Student> Student { get; set; } public virtual DbSet<StudentAddress> StudentAddress { get; set; } public virtual DbSet<StudentCourse> StudentCourse { get; set; } public virtual DbSet<Teacher> Teacher { get; set; } protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder) { if (!optionsBuilder.IsConfigured) { #warning To protect potentially sensitive information in your connection string, you should move it out of source code. See http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=723263 for guidance on storing connection strings. optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer(@"Server=.\SQLExpress;Database=SchoolDB;Trusted_Connection=True;"); } } protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder) { modelBuilder.Entity<Course>(entity => { entity.Property(e => e.CourseName) .HasMaxLength(50) .IsUnicode(false); entity.HasOne(d => d.Teacher) .WithMany(p => p.Course) .HasForeignKey(d => d.TeacherId) .OnDelete(DeleteBehavior.Cascade) .HasConstraintName("FK_Course_Teacher"); }); modelBuilder.Entity<Standard>(entity => { entity.Property(e => e.Description) .HasMaxLength(50) .IsUnicode(false); entity.Property(e => e.StandardName) .HasMaxLength(50) .IsUnicode(false); }); modelBuilder.Entity<Student>(entity => { entity.Property(e => e.StudentId).HasColumnName("StudentID"); entity.Property(e => e.FirstName) .HasMaxLength(50) .IsUnicode(false); entity.Property(e => e.LastName) .HasMaxLength(50) .IsUnicode(false); entity.HasOne(d => d.Standard) .WithMany(p => p.Student) .HasForeignKey(d => d.StandardId) .OnDelete(DeleteBehavior.Cascade) .HasConstraintName("FK_Student_Standard"); }); modelBuilder.Entity<StudentAddress>(entity => { entity.HasKey(e => e.StudentId); entity.Property(e => e.StudentId) .HasColumnName("StudentID") .ValueGeneratedNever(); entity.Property(e => e.Address1) .IsRequired() .HasMaxLength(50) .IsUnicode(false); entity.Property(e => e.Address2) .HasMaxLength(50) .IsUnicode(false); entity.Property(e => e.City) .IsRequired() .HasMaxLength(50) .IsUnicode(false); entity.Property(e => e.State) .IsRequired() .HasMaxLength(50) .IsUnicode(false); entity.HasOne(d => d.Student) .WithOne(p => p.StudentAddress) .HasForeignKey<StudentAddress>(d => d.StudentId) .HasConstraintName("FK_StudentAddress_Student"); }); modelBuilder.Entity<StudentCourse>(entity => { entity.HasKey(e => new { e.StudentId, e.CourseId }); entity.HasOne(d => d.Course) .WithMany(p => p.StudentCourse) .HasForeignKey(d => d.CourseId) .OnDelete(DeleteBehavior.ClientSetNull) .HasConstraintName("FK_StudentCourse_Course"); entity.HasOne(d => d.Student) .WithMany(p => p.StudentCourse) .HasForeignKey(d => d.StudentId) .HasConstraintName("FK_StudentCourse_Student"); }); modelBuilder.Entity<Teacher>(entity => { entity.Property(e => e.StandardId).HasDefaultValueSql("((0))"); entity.Property(e => e.TeacherName) .HasMaxLength(50) .IsUnicode(false); entity.HasOne(d => d.Standard) .WithMany(p => p.Teacher) .HasForeignKey(d => d.StandardId) .OnDelete(DeleteBehavior.Cascade) .HasConstraintName("FK_Teacher_Standard"); }); } } }
Note: EF Core creates entity classes only for tables and not for StoredProcedures or Views.
DotNet CLI
If you use dotnet command line interface to execute EF Core commands then open command prompt and navigate to the root folder and execute the following dotnet ef dbcontext scaffold command:
> dotnet ef dbcontext scaffold "Server=.\SQLEXPRESS;Database=SchoolDB;Trusted_Connection=True;" Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer -o Models Thus, you can create EF Core model for an existing database.
Note: Once you have created the model, you must use the Migration commands whenever you change the model to keep the database up to date with the model.
How To Create Dbcontext In Entity Framework Core
Source: https://www.entityframeworktutorial.net/efcore/create-model-for-existing-database-in-ef-core.aspx
Posted by: cochranhaustrand.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Create Dbcontext In Entity Framework Core"
Post a Comment